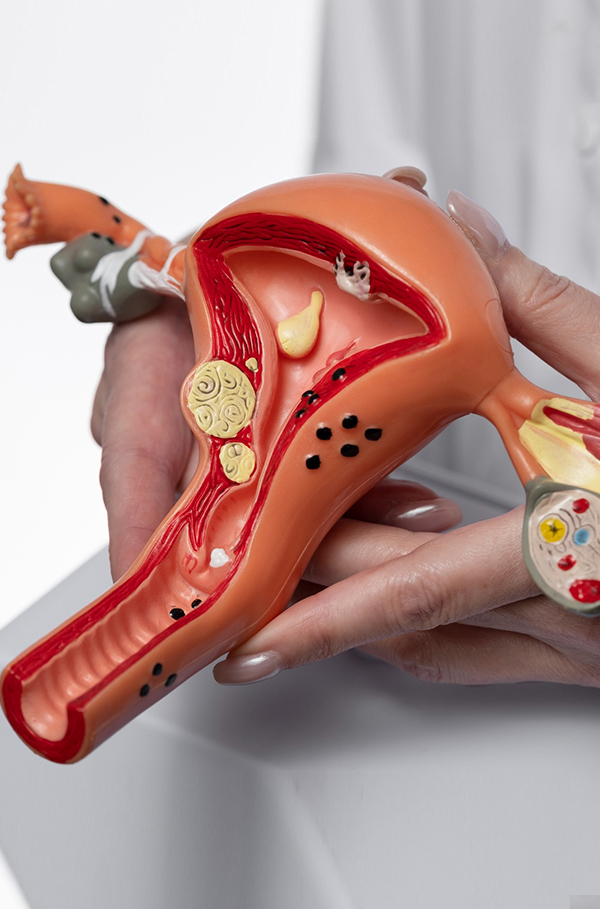
Cancer screening plays a critical role in identifying cancers at an early stage when treatment is more effective. Among these, the Pap smear test, also known as the Papanicolaou test, is a routine procedure used to screen for cervical cancer in women. It can also detect precancerous changes in the cervix, helping prevent the progression to cancer.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer often shows no symptoms in its early stages, which underscores the importance of regular screening. When symptoms do appear, they may include:
Causes of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is primarily caused by persistent infection with high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted virus. Other factors that increase the risk include:
The Role of the Pap Smear
A Pap smear is a simple, quick, and non-invasive test. It involves collecting cells from the cervix to check for abnormalities. Women aged 21–65 are advised to undergo regular screening, with the frequency depending on age, medical history, and the results of previous tests.
Diagnosis and Treatments
If abnormal cells are detected during a Pap smear, further tests like HPV testing, colposcopy, or biopsy may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment depends on the stage of the disease:
Prevention
